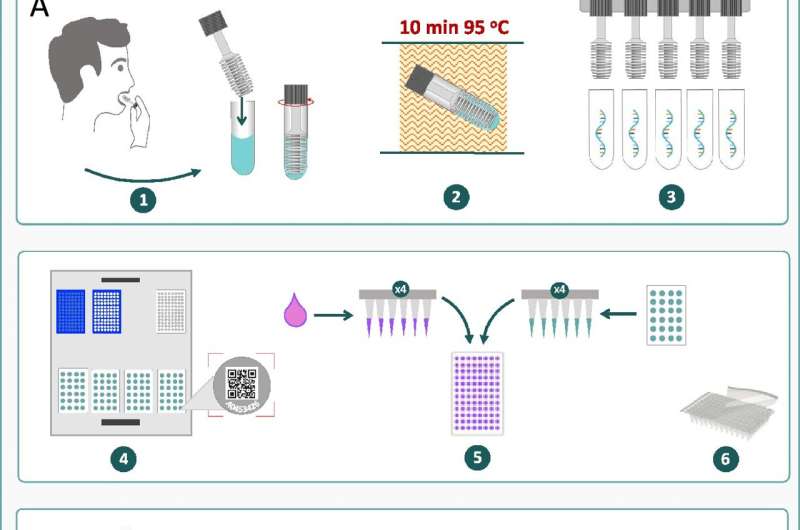
The latest research from Murdoch University and the Perron Institute is paving the way for the development of a new technological screening platform that will rapidly and accurately detect COVID-19, without compromising quality.
The Avicena Sentinel saliva sampling approach involves sensitive molecular processes and ultra-high throughput technology for screening potentially infectious, asymptomatic carriers.
It can run up to four thousand samples per hour, with results reported within 25 minutes.
Latest data published in the Nature journal Scientific Reports shows 98% accuracy in identifying the SARS-CoV-2 virus in samples.
Senior author, Professor Sulev Koks, Head of Genetic Epidemiology Research at Murdoch University and at Western Australia’s Perron Institute, is among the scientists and others contributing.
He is collaborating with local specialists from Avicena Systems, Telethon Kids Institute, The University Western Australia and further afield in the United Kingdom and Spain. The key overseas organizations evaluating the technology are the Lancs LAMP Laboratory in Preston, UK and Biodonostia Health Research Institute in San Sebastian, Spain.
Professor Koks said although present testing methods are accurate, they are not capable of providing a result to people with COVID-19 that have no symptoms. Additionally, PCR testing puts a strain on the health system as health staff need to undertake rigorous training to obtain results.
“The rapid antigen tests (RAT) are easier to use but not sufficiently sensitive in detecting the virus in infected people who are contagious but have no symptoms. The viral load samples from presymptomatic or asymptomatic people can take several days to reach sufficient levels for detecting infection.
“PCR results take hours and throughput is, at most, a few thousand samples processed per instrument per day. Also, nasopharyngeal PCR sampling requires trained personnel and has decreased participant acceptance if multiple testings are required within a short period.
“Effective viral surveillance to contain outbreaks requires frequent testing with more sensitive assays, particularly as new variants arise.”
Professor Koks explained the new screening technology, that will identify infectious patients sooner and eliminate the threat of unwanted community transmission, will help hasten the pandemic’s closure.
“The proposed large-scale and convenient saliva testing platform combines accuracy and scalability to mitigate the risk of viral transmission as restrictions are lifted and to guard against future threats.
“It would make frequent testing feasible in complementing vaccines to contain the spread of highly infectious pandemic agents such as COVID-19.”
Further validation of Avicena’s rapid, ultra-sensitive Sentinel screening system is continuing.
Source: Read Full Article