The repurposing of FDA-approved drugs for alternative diseases is a faster way of bringing new treatments into the clinic. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have repurposed a cancer drug for treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis. A novel drug carrier was also developed to facilitate drug delivery to target myeloid cells. These pre-clinical findings are described in a paper in the journal EMBO Reports.
Microglia are an organ-specific type of macrophage in the central nervous system. In the majority of chronic neurodegenerative disease conditions, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s disease and chronic multiple sclerosis (MS), dysfunctional microglia play an important role. Modifying the activation of these disease-promoting microglia is an attractive therapeutic principle.
“The biotechnology industry has realized the potential for microglia-targeting strategies, and at least 20 new companies have started during recent years,” says Professor Bob Harris at the Center for Molecular Medicine, Karolinska University Hospital and the Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet. “Compared to novel drug discovery programs that can take 20 years before a new medicine is approved, using existing prescribed drugs can halve that time.”
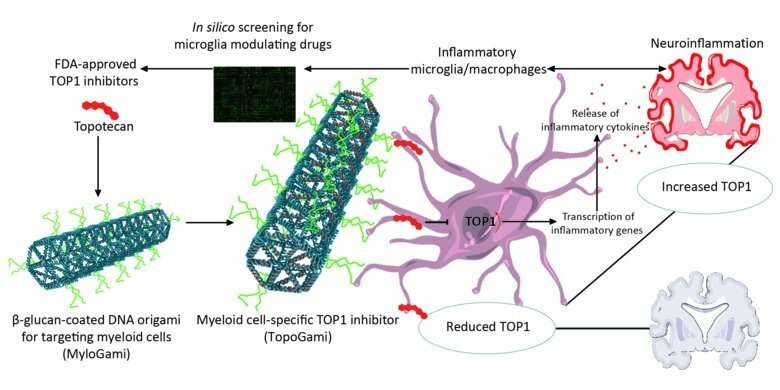
The researchers used in silico drug screening to identify candidates for microglial modulation and selected a Topoisomerase 1 (TOP1) inhibitor for further study. TOP1 was highly expressed in neuroinflammatory conditions both in mice and in tissues from MS patients, and TOP1 inhibition using camptothecin (CPT) and its FDA-approved analog topotecan (TPT) reduced inflammatory responses in microglia and macrophages in in vitro cultures, as well as ameliorating neuroinflammatory diseases in vivo.
Old drugs become new drugs
“The data-mining of open access databases is an approach that is both time and economically efficient, and there is so much data available nowadays,” says first author Keying Zhu, doctoral student at the Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet. “We were lucky to identify four compounds with the properties we wished for, and one of these proved to be promising for our continued investigations, ultimately demonstrating significant therapeutic effect in our experimental model of MS.”
Source: Read Full Article