Researchers in Singapore have conducted a study showing that the messenger RNA- (mRNA) based coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna are highly effective at protecting against symptomatic and severe disease following infection with the rapidly spreading B.1.617.2 (delta) variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The team conducted a multi-center retrospective cohort study of vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals who had been admitted to hospital following infection with the B.1.617.2 variant of concern.
“To our knowledge, we provide the first data characterizing the impact of vaccination on virologic kinetics by the B.1.617.2 variant,” writes Barnaby Young from the National Centre for Infectious Diseases in Singapore and colleagues.
The team found that individuals fully vaccinated with either Pfizer-BioNTech’s BNT162b2 vaccine or Moderna’s mRNA-1273 product were significantly less likely to develop moderate or severe outcomes following B.1.617.2 infection than unvaccinated individuals.
Vaccination was associated with fewer symptoms, lower peak biomarkers of systemic inflammation, and better clinical outcomes. It was also associated with a more rapid decline in viral RNA load and a robust serologic response.
“Vaccination remains a key strategy for control of COVID-19 pandemic,” says Young and colleagues.
A pre-print version of the research paper isa available on the medRxiv* server, while the article undergoes peer review.
.jpg)
Variants of concern pose a threat to vaccination efforts
Phase 3 clinical trials of mRNA-based vaccines have demonstrated efficacies of 92% to 95% in preventing symptomatic and severe disease following SARS-CoV-2 infection.
While the mass rollout of these vaccines has reduced infection and mortality rates in many countries, the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants containing mutations in the viral spike protein has led to growing concerns regarding increased transmissibility and resistance to vaccine-induced immunity.
The spike protein is the main structure the virus uses to infect cells and a primary target of binding and neutralizing antibodies following natural infection or vaccination.
While variants of concern such as B.1.1.7 (alpha), B.1.351 (beta), P.1 (gamma), and B.1.617.2 (delta) have all been shown to exhibit increased transmissibility, the B.1.1.7 and B.1.617.2 strains have also been associated with increased disease severity and hospitalization.
Following the emergence of B.1.617.2 in India, this variant rapidly spread to other countries and had become the most frequently sequenced lineage worldwide by the end of June 2021.
The vaccination program in Singapore
The COVID-19 vaccination program began in Singapore on December 30th, 2020. Free vaccination with either the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna product was made available to all Singapore residents, beginning with the elderly and those with high-risk occupations such as healthcare workers.
As of July 19th, 2021, more than 6,837,000 vaccine doses had been administered and approximately 2,792,400 individuals had been fully vaccinated.
What did the researchers do?
Young and colleagues conducted a multi-center retrospective cohort study to characterize the clinical, virologic and serologic features of vaccinated adults with breakthrough B.1.617.2 infection. The results were compared with those of unvaccinated patients who also had B.1.617.2 infection.
Participants were recruited between April 1st and June 14th, 2021, across five study sites: the National Centre for Infectious Diseases, Singapore General Hospital, National University Hospital, Changi General Hospital and Sengkang Hospital.
What did the study find?
Of 218 individuals diagnosed with B.1.617.2 infection by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing, 88 had received a vaccine.
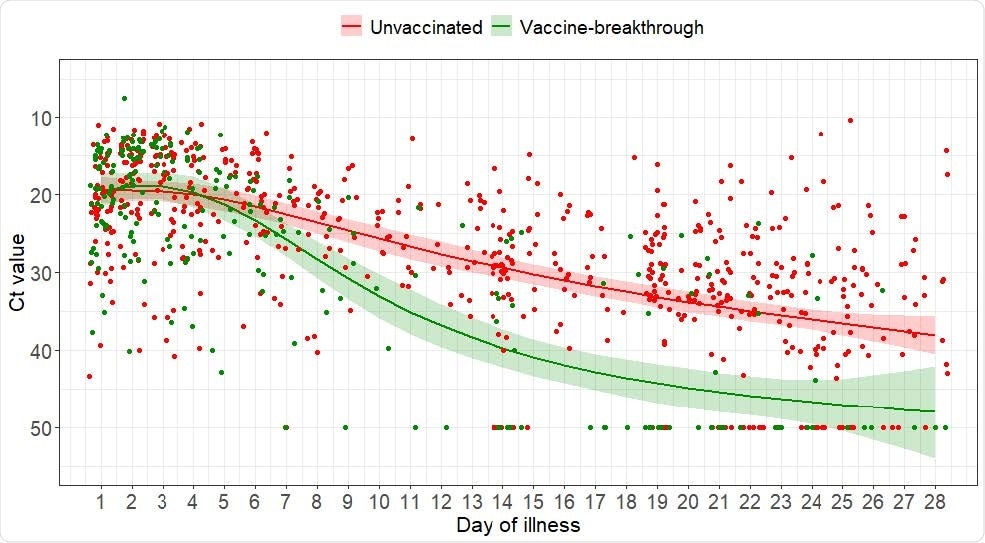
Seventy-one individuals were fully vaccinated and therefore met the definition for vaccine-breakthrough infection. Sixty-six of these participants (93%) had received two doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine.
The vaccine-breakthrough infection cohort was significantly older than the unvaccinated cohort, at a median of 56 years (age range 39 to 64) versus 39.5 years (age range 30 to 58). Individuals with breakthrough infection were also significantly more likely to be asymptomatic (at 28.2% versus 9.2%) and to have fewer symptoms if they were symptomatic.
Unvaccinated individuals had higher levels of biomarkers known to be associated with more severe disease, including lymphocyte count, C-reactive protein, lactate dehydrogenase and alanine transferase.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that vaccinated individuals were 97% less likely to develop severe COVID-19 that required oxygen supplementation or moderate disease (defined as development of pneumonia).
“The finding of diminished severity with B.1.617.2 infection in vaccinated individuals is reassuring and corroborates emerging data from the United Kingdom which have found that mRNA vaccination remains protective against symptomatic and severe disease,” says the team.
More about the virologic kinetics
The initial PCR cycle threshold (Ct) values (number of cycles required for virus detection) were similar between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups, at 19.2 versus 18.8.
However, the median Ct value increased more rapidly over time among vaccinated individuals, pointing to a faster decline in viral load.
The researchers say this has implications in terms of transmissibility and infection control policy.
“A shorter duration of infectivity may allow a shorter duration of isolation for vaccinated individuals,” they write.
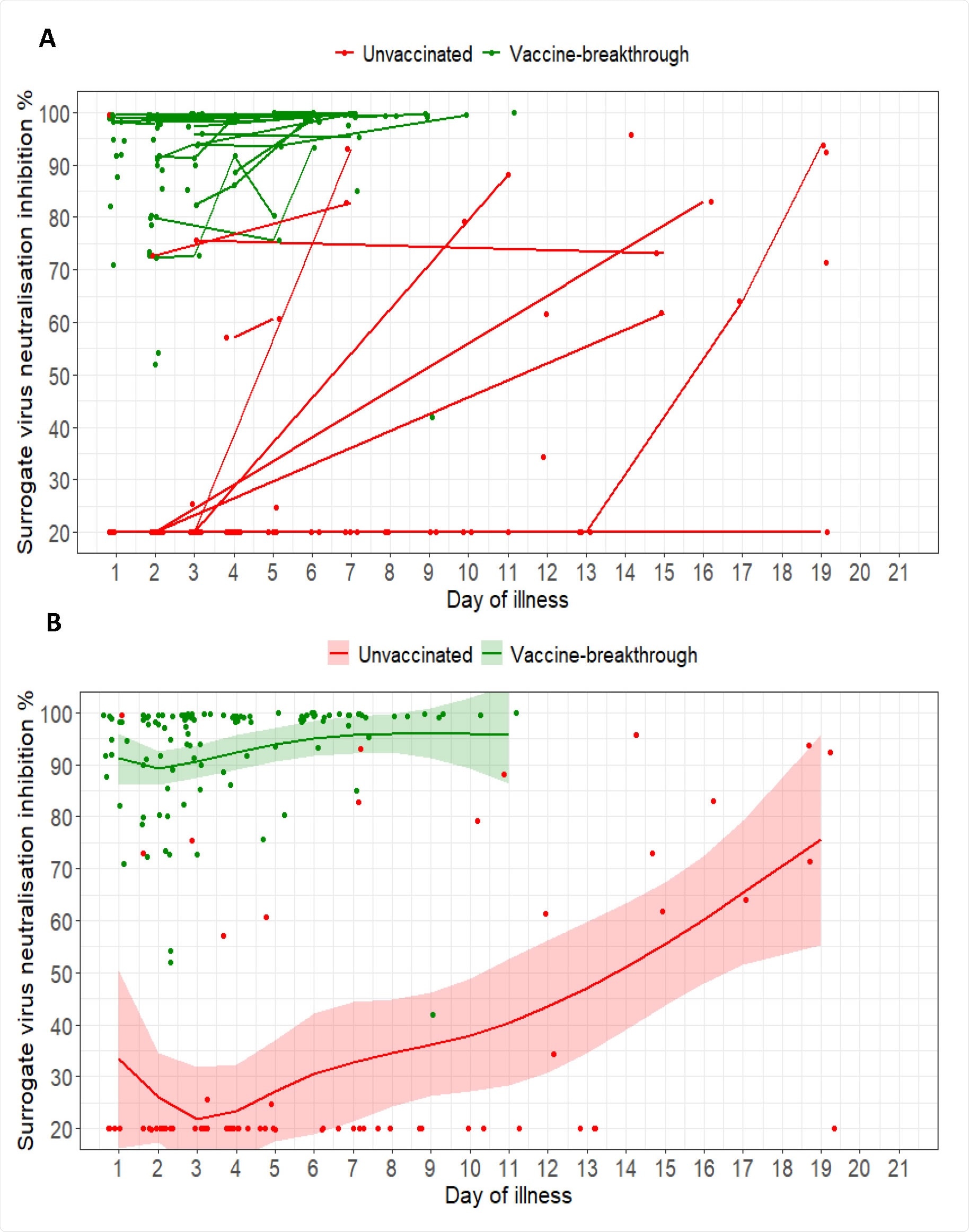
More about the serologic findings
Of 66 vaccinated individuals with available serologic data, all (100%) had detectable anti-spike antibodies during the first week of illness, compared with seven (16%) of 45 unvaccinated individuals.
“The mRNA vaccines are highly effective at preventing symptomatic and severe COVID-19 associated with B.1.617.2 infection,” says Young and colleagues. “Vaccination is associated with faster decline in viral RNA load and a robust serological response.”
The researchers say that while vaccine-breakthrough infections will continue to be observed, it is likely that there will be a shift towards a milder disease spectrum with more widespread implementation of vaccination programs.
“Rapid and widespread implementation of vaccination programs remains a key strategy for control of the COVID-19 pandemic,” they conclude.
*Important Notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
- Young B, et al. Virological and serological kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant vaccine-breakthrough infections: a multi-center cohort study. medRxiv, 2021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.28.21261295, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.28.21261295v1
Posted in: Men's Health News | Medical Research News | Women's Health News | Disease/Infection News
Tags: Alanine, Antibodies, Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, C-Reactive Protein, CT, Efficacy, Healthcare, Hospital, immunity, Infection Control, Infectious Diseases, Inflammation, Lymphocyte, Mortality, Oxygen, Pandemic, Pneumonia, Polymerase, Polymerase Chain Reaction, Protein, Research, Respiratory, RNA, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Spike Protein, Syndrome, Vaccine, Virus

Written by
Sally Robertson
Sally first developed an interest in medical communications when she took on the role of Journal Development Editor for BioMed Central (BMC), after having graduated with a degree in biomedical science from Greenwich University.
Source: Read Full Article